ZIKA Virus
Zika virus
(ZIKV) is a member of the Flaviviridae virus family and the Flavivirus genus.
In humans, it initially causes a mild illness known as Zika fever, Zika, or Zika disease, which
since the 1950s has been known to occur within a narrow equatorial belt from
Africa to Asia. In 2014, the virus spread eastward across the Pacific Ocean to French Polynesia, then to Easter
Island and in 2015 to Central America, the Caribbean, and South
America, where the Zika
outbreak has reached pandemic levels.
| Illustration of Zika Virus. |
Zika
virus is related to dengue, yellow
fever, Japanese
encephalitis, and West
Nile viruses. The illness it causes is similar to a mild form
of dengue fever, is
treated by rest, and
cannot yet be prevented by drugs or vaccines. There is a possible link between
Zika fever and microcephaly in newborn babies by mother-to-child
transmission, as
well as a stronger one with neurologic conditions in infected adults, including
cases of the Guillain–Barré
syndrome.
Affected Areas [till
now]-
AMERICAS
·
Barbados
·
Bolivia
·
Brazil
·
Colombia
·
Dominican Republic
·
Ecuador
·
El Salvador
·
French Guiana
·
Guadeloupe
·
Guatemala
·
Guyana
·
Haiti
·
Honduras
·
Martinique
·
Mexico
·
Panama
·
Paraguay
·
Puerto Rico
·
Saint Martin
·
Suriname
·
U.S. Virgin Islands
·
Venezuela
OCEANIA/PACIFIC ISLANDS
·
Samoa
AFRICA
·
Cape Verde
How they Transmitted?
Zika virus is transmitted by daytime-active mosquitoes and
has been isolated from a number of species in the genus Aedes,
such as A. aegypti, and arboreal mosquitoes such as A.
africanus, A. apicoargenteus, A. furcifer, A. hensilli, A. luteocephalus, and A. vitattus. Studies show that the extrinsic incubation
period in mosquitoes is about 10 days. Zika virus can
migrate between humans through sexual contact and it can also cross the
placenta, affecting an unborn fetus. A mother already infected with Zika virus
near the time of delivery can pass on the virus to her newborn around the time
of birth.
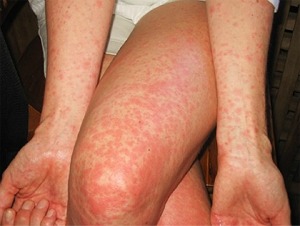 |
| Rash |
What are symptoms of Zika virus infection?
| Red eyes |
About 1 in 5 people infected with Zika virus
become symptomatic. Clinical illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting for
several days to a week.
·
About 1 in 5 people infected with Zika
virus become ill (i.e., develop Zika).
·
The most common symptoms of Zika are
fever, rash, joint pain, or conjunctivitis (red eyes). Other common symptoms
include muscle pain and headache. The incubation period (the time from exposure
to symptoms) for Zika virus disease is not known, but is likely to be a few
days to a week.
·
The illness is usually mild with symptoms
lasting for several days to a week.
·
Zika virus usually remains in the blood of
an infected person for a few days but it can be found longer in some people.
·
Severe disease requiring hospitalization
is uncommon.
·
Deaths are rare.
How to Diagnose?
During the first week after onset of symptoms, Zika virus disease can
often be diagnosed by performing reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain
reaction (RT-PCR) on serum.
How can Zika virus infection be prevented?
There is no vaccine to prevent Zika virus
infection. Travelers can protect themselves by taking steps to prevent mosquito bites. Use
insect repellent; wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants; and stay in places
with air conditioning or with window and door screens. Pregnant women can and
should choose an EPA-registered insect repellent and use it according to the
product label.
Treatment
·
No vaccine or medications are available to
prevent or treat Zika infections.
·
Treat the symptoms:
o
Get plenty of rest
o
Drink fluids to prevent dehydration
o
Take medicine such as acetaminophen to
relieve fever and pain
o
Do not take aspirin and other
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen and naproxen.
Aspirin and NSAIDs should be avoided until dengue can be ruled out to reduce
the risk of hemorrhage (bleeding). If you are taking medicine for another
medical condition, talk to your healthcare provider before taking additional
medication.
·
If you have Zika, avoid mosquito bites for
the first week of your illness.
o
During the first week of infection, Zika
virus can be found in the blood and passed from an infected person to another
mosquito through mosquito bites.
o
An infected mosquito can then spread the
virus to other people.
Comments
Post a Comment